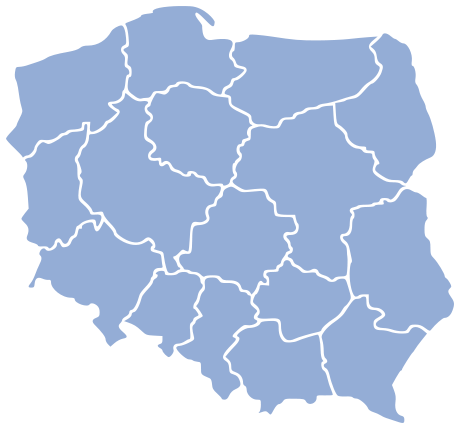
Voivodeships of Poland
 |
| Administrative division of Poland |
|---|
| Voivodeships Powiats (list) Gminas (list) |
The voivodeship or province (Polish: województwo) has been a high-level administrative subdivision of Poland since the 14th century. Pursuant to the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998, which came into effect on January 1, 1999, sixteen new voivodeships were created. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from July 1, 1975.
Today's voivodeships are largely based on the country's historic regions, while those of 1975–1998 were centred on and named for individual cities. The new units range in area from under 10,000 km2 (3,900 sq mi) (Opole Voivodeship) to over 35,000 km2 (14,000 sq mi) (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from one million (Lubusz Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship).
Administrative authority at voivodeship level is shared between a government-appointed governor called a voivode (Polish wojewoda), an elected assembly called a sejmik, and an executive chosen by that assembly. The leader of that executive is called the marszałek województwa (voivodeship marshal). Voivodeships are further divided into powiats (counties) and gminas (communes or municipalities): see Administrative division of Poland.
Voivodeships since 1999
Administrative powers
Competences and powers at voivodeship level are shared between the voivode (governor), the sejmik (regional assembly) and the executive. In most cases these institutions are all based in one city, but in Kuyavian-Pomeranian and Lubusz Voivodeship the voivode's offices are in a different city from those of the executive and the sejmik. Voivodeship capitals are listed in the table below.
The voivode is appointed by the Prime Minister and is the regional representative of the central government. The voivode acts as the head of central government institutions at regional level (such as the police and fire services, passport offices, and various inspectorates), manages central government property in the region, oversees the functioning of local government, coordinates actions in the field of public safety and environment protection, and exercises special powers in emergencies. The voivode's offices collectively are known as the urząd wojewódzki.
The sejmik is elected every four years, at the same time as the local authorities at powiat and gmina level. It passes bylaws, including the voivodeship's development strategies and budget. It also elects the marszałek and other members of the executive, and holds them to account.
The executive (zarząd województwa), headed by the marszałek, drafts the budget and development strategies, implements the resolutions of the sejmik, manages the voivodeship's property, and deals with many aspects of regional policy, including management of European Union funding. Its offices collectively are known as the urząd marszałkowski.
Map and table of voivodeships
 |
|||||||
| Polish voivodeships since 1999 | |||||||
| Abbreviation | code | car plates |
Voivodeship | Capital | Area km² | Population (December 31, 2003) |
Population (June 30, 2004) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DS | 02 | D | Lower Silesian (dolnośląskie) | Wrocław | 19 947.76 | 2 898 313 | 2 895 729 |
| KP | 04 | C | Kuyavian-Pomeranian (kujawsko-pomorskie) | Bydgoszcz¹ Toruń² |
17 969.72 | 2 068 142 | 2 067 548 |
| LU | 06 | L | Lublin (lubelskie) | Lublin | 25 114.48 | 2 191 172 | 2 187 918 |
| LB | 08 | F | Lubusz (lubuskie) | Gorzów Wielkopolski¹ Zielona Góra² |
13 984.44 | 1 008 786 | 1 009 177 |
| LD | 10 | E | Łódź (łódzkie) | Łódź | 18 219.11 | 2 597 094 | 2 592 568 |
| MP | 12 | K | Lesser Poland (małopolskie) | Kraków | 15 144.10 | 3 252 949 | 3 256 171 |
| MA | 14 | W | Masovian (mazowieckie) | Warsaw | 35 597.80 | 5 135 732 | 5 139 545 |
| OP | 16 | O | Opole (opolskie) | Opole | 9 412.47 | 1 055 667 | 1 053 723 |
| PK | 18 | R | Subcarpathian (podkarpackie) | Rzeszów | 17 926.28 | 2 097 248 | 2 097 325 |
| PD | 20 | B | Podlaskie (podlaskie) | Białystok | 20 179.58 | 1 205 117 | 1 204 036 |
| PM | 22 | G | Pomeranian (pomorskie) | Gdańsk | 18 292.88 | 2 188 918 | 2 192 404 |
| SL | 24 | S | Silesian (śląskie) | Katowice | 12 294.04 | 4 714 982 | 4 707 825 |
| SW | 26 | T | Świętokrzyskie | Kielce | 11 672.34 | 1 291 598 | 1 290 176 |
| WM | 28 | N | Warmian-Masurian (warmińsko-mazurskie) | Olsztyn | 24 202.95 | 1 428 885 | 1 428 385 |
| WP | 30 | P | Greater Poland (wielkopolskie) | Poznań | 29 825.59 | 3 359 932 | 3 362 011 |
| ZP | 32 | Z | West Pomeranian (zachodniopomorskie) | Szczecin | 22 901.48 | 1 696 073 | 1 695 708 |
| (¹) – seat of voivode, (²) – seat of sejmik and marszałek | |||||||
| Poland |
 This article is part of the series: |
|
|
|
Government
Judiciary
Elections
Political parties
Foreign policy
See also
|
|
Other countries · Atlas |
-
- See also:
- Map of Polish Regions
- Administrative division of Poland (from Commission on Standardization of Geographical Names Outside Poland website, in English)
- Official map by Head Office of Geodesy and Cartography
Former voivodeships
Poland's voivodeships 1975-1998 (49 voivodeships)
(since 1989, the Third Polish Republic)
See also Administrative division of People's Republic of Poland)
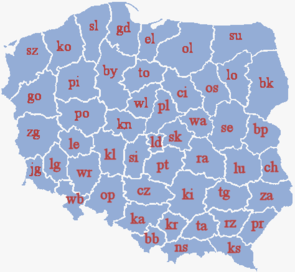
This reorganization of administrative division of Poland was mainly a result of local government reform acts of 1973–1975. In place of the three-level administrative division (voivodeship, county, commune), a new two-level administrative division was introduced (49 small voivodeships, and communes). The three smallest voivodeships – Warsaw, Kraków and Łódź – had the special status of municipal voivodeship; the city president (mayor) was also provincial governor.
| Polish voivodeships and separate cities 1975-1998 | |||||||
| Abbreviation | Voivodeship | Polish name | Capital | Area km² (1998) |
Population (1980) |
No. of cities | No. of communes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bp | Biała Podlaska Voivodeship | bialskopodlaskie | Biała Podlaska | 5 348 | 286 400 | 6 | 35 |
| bk | Białystok Voivodeship | białostockie | Białystok | 10 055 | 641 100 | 17 | 49 |
| bb | Bielsko-Biała Voivodeship | bielskie | Bielsko-Biała | 3 704 | 829 900 | 18 | 47 |
| by | Bydgoszcz Voivodeship | bydgoskie | Bydgoszcz | 10 349 | 1 036 000 | 27 | 55 |
| ch | Chełm Voivodeship | chełmskie | Chełm | 3 865 | 230 900 | 4 | 25 |
| ci | Ciechanów Voivodeship | ciechanowskie | Ciechanów | 6 362 | 405 400 | 9 | 45 |
| cz | Częstochowa Voivodeship | częstochowskie | Częstochowa | 6 182 | 747 900 | 17 | 49 |
| el | Elbląg Voivodeship | elbląskie | Elbląg | 6 103 | 441 500 | 15 | 37 |
| gd | Gdańsk Voivodeship | gdańskie | Gdańsk | 7 394 | 1 333 800 | 19 | 43 |
| go | Gorzów Voivodeship | gorzowskie | Gorzów Wielkopolski | 8 484 | 455 400 | 21 | 38 |
| jg | Jelenia Góra Voivodeship | jeleniogórskie | Jelenia Góra | 4 378 | 492 600 | 24 | 28 |
| kl | Kalisz Voivodeship | kaliskie | Kalisz | 6 512 | 668 000 | 20 | 53 |
| ka | Katowice Voivodeship | katowickie | Katowice | 6 650 | 3 733 900 | 43 | 46 |
| ki | Kielce Voivodeship | kieleckie | Kielce | 9 211 | 1 068 700 | 17 | 69 |
| kn | Konin Voivodeship | konińskie | Konin | 5 139 | 441 200 | 18 | 43 |
| ko | Koszalin Voivodeship | koszalińskie | Koszalin | 8 470 | 462 200 | 17 | 35 |
| kr | Kraków Voivodeship | krakowskie | Kraków | 3 254 | 1 167 500 | 10 | 38 |
| ks | Krosno Voivodeship | krośnieńskie | Krosno | 5 702 | 448 200 | 12 | 37 |
| lg | Legnica Voivodeship | legnickie | Legnica | 4 037 | 458 900 | 11 | 31 |
| le | Leszno Voivodeship | leszczyńskie | Leszno | 4 254 | 357 600 | 19 | 28 |
| lu | Lublin Voivodeship | lubelskie | Lublin | 6 793 | 935 200 | 16 | 62 |
| lo | Łomża Voivodeship | łomżyńskie | Łomża | 6 684 | 325 800 | 12 | 39 |
| ld | Łódź Voivodeship | łódzkie | Łódź | 1523 | 1 127 800 | 8 | 11 |
| ns | Nowy Sącz Voivodeship | nowosądeckie | Nowy Sącz | 5 576 | 628 800 | 14 | 41 |
| ol | Olsztyn Voivodeship | olsztyńskie | Olsztyn | 12 327 | 681 400 | 21 | 48 |
| op | Opole Voivodeship | opolskie | Opole | 8 535 | 975 000 | 29 | 61 |
| os | Ostrołęka Voivodeship | ostrołęckie | Ostrołęka | 6 498 | 371 400 | 9 | 38 |
| pi | Piła Voivodeship | pilskie | Piła | 8 205 | 437 100 | 24 | 35 |
| pt | Piotrków Voivodeship | piotrkowskie | Piotrków Trybunalski | 6 266 | 604 200 | 10 | 51 |
| pl | Płock Voivodeship | płockie | Płock | 5 117 | 496 100 | 9 | 44 |
| po | Poznań Voivodeship | poznańskie | Poznań | 8 151 | 1 237 800 | 33 | 57 |
| pr | Przemyśl Voivodeship | przemyskie | Przemyśl | 4 437 | 380 000 | 9 | 35 |
| rs | Radom Voivodeship | radomskie | Radom | 7 295 | 702 300 | 15 | 61 |
| rz | Rzeszów Voivodeship | rzeszowskie | Rzeszów | 4 397 | 648 900 | 13 | 41 |
| se | Siedlce Voivodeship | siedleckie | Siedlce | 8 499 | 616 300 | 12 | 66 |
| si | Sieradz Voivodeship | sieradzkie | Sieradz | 4 869 | 392 300 | 9 | 40 |
| sk | Skierniewice Voivodeship | skierniewickie | Skierniewice | 3 959 | 396 900 | 8 | 36 |
| sl | Słupsk Voivodeship | słupskie | Słupsk | 7 453 | 369 800 | 11 | 31 |
| su | Suwałki Voivodeship | suwalskie | Suwałki | 10 490 | 422 600 | 14 | 42 |
| sz | Szczecin Voivodeship | szczecińskie | Szczecin | 9 981 | 897 900 | 29 | 50 |
| tg | Tarnobrzeg Voivodeship | tarnobrzeskie | Tarnobrzeg | 6 283 | 556 300 | 14 | 46 |
| ta | Tarnów Voivodeship | tarnowskie | Tarnów | 4 151 | 607 000 | 9 | 41 |
| to | Toruń Voivodeship | toruńskie | Toruń | 5 348 | 610 800 | 13 | 41 |
| wb | Wałbrzych Voivodeship | wałbrzyskie | Wałbrzych | 4 168 | 716 100 | 31 | 30 |
| wa | Warsaw Voivodeship | warszawskie | Warsaw | 3 788 | 2 319 100 | 27 | 32 |
| wl | Włocławek Voivodeship | włocławskie | Włocławek | 4 402 | 413 400 | 14 | 30 |
| wr | Wrocław Voivodeship | wrocławskie | Wrocław | 6 287 | 1 076 200 | 16 | 33 |
| za | Zamość Voivodeship | zamojskie | Zamość | 6 980 | 472 100 | 5 | 47 |
| zg | Zielona Góra Voivodeship | zielonogórskie | Zielona Góra | 8 868 | 609 200 | 26 | 50 |
Poland's voivodeships 1945-1975 (14+2 voivodeships, then 17+5)
Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of Poland
After World War II, the new administrative division of the country was based on the prewar one. The areas in the east that had not been annexed by the Soviet Union had their borders left almost unchanged. The newly acquired territories in the west and north were organized into the voivodeships of Szczecin, Wrocław and Olsztyn, and partly joined to Gdańsk, Katowice and Poznań voivodeships. Two cities were granted voivodeship status: Warsaw and Łódź.
In 1950, new voivodeships were created: Koszalin (previously part of Szczecin), Opole (previously part of Katowice), and Zielona Góra (previously part of Poznań, Wrocław and Szczecin voivodeships). In addition, three more cities were granted voivodeship status: Wrocław, Kraków and Poznań.
| Polish administrative division 1945-1975 | ||||
| Car plates (since 1956) |
Voivodeship | Capital | Area km² (1965) |
Population (1965) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | białostockie | Białystok | 23 136 | 1 160 400 |
| B | bydgoskie | Bydgoszcz | 20 794 | 1 837 100 |
| G | gdańskie | Gdańsk | 10 984 | 1 352 800 |
| S | katowickie | Katowice | 9 518 | 3 524 300 |
| C | kieleckie | Kielce | 19 498 | 1 899 100 |
| E | koszalińskie ¹ | Koszalin | 17 974 | 755 100 |
| K | krakowskie | Kraków | 15 350 | 2 127 600 |
| F | Łódzkie | Łódź | 17 064 | 1 665 200 |
| L | lubelskie | Lublin | 24 829 | 1 900 500 |
| O | olsztyńskie | Olsztyn | 20 994 | 956 600 |
| H | opolskie ¹ | Opole | 9 506 | 1 009 200 |
| P | poznańskie | Poznań | 26 723 | 2 126 300 |
| R | rzeszowskie | Rzeszów | 18 658 | 1 692 800 |
| M | szczecińskie | Szczecin | 12 677 | 847 600 |
| T | warszawskie | Warsaw | 29 369 | 2 453 000 |
| X | wrocławskie | Wrocław | 18 827 | 1 967 000 |
| Z | zielonogórskie ¹ | Zielona Góra | 14 514 | 847 200 |
| car plates (since 1956) |
Separate city | Area km² (1965) |
Population (1965) |
|
| I | Łódź | 214 | 744 100 | |
| W | Warsaw | 446 | 1 252 600 | |
| ? | Kraków ² | 230 | 520 100 | |
| ? | Poznań ² | 220 | 438 200 | |
| ? | Wrocław ² | 225 | 474 200 | |
| ¹ – new voivodeships created in 1950; ² – cities separated in 1957 | ||||
Poland's voivodeships 1921-1939 (15+1 voivodeships +1 Autonomous Silesian)
| Polish voivodeships in the interbellum (data as per April 1, 1937) |
||||||
| car plates (since 1937) |
Voivodeship Separate city |
Capital | Area in 1000 km² (1930) |
Population in 1000 (1931) |
Map | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00-19 | City of Warsaw | Warsaw | 0.14 | 1179.5 | 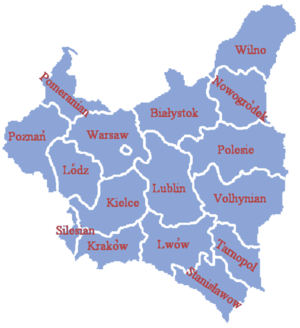 |
|
| 85-89 | warszawskie | Warsaw | 31.7 | 2460.9 | ||
| 20-24 | białostockie | Białystok | 26.0 | 1263.3 | ||
| 25-29 | kieleckie | Kielce | 22.2 | 2671.0 | ||
| 30-34 | krakowskie | Kraków | 17.6 | 2300.1 | ||
| 35-39 | lubelskie | Lublin | 26.6 | 2116.2 | ||
| 40-44 | lwowskie | Lwów | 28.4 | 3126.3 | ||
| 45-49 | łódzkie | Łódź | 20.4 | 2650.1 | ||
| 50-54 | nowogródzkie | Nowogródek | 23.0 | 1057.2 | ||
| 55-59 | poleskie | Brześć nad Bugiem | 36.7 | 1132.2 | ||
| 60-64 | pomorskie | Toruń | 25.7 | 1884.4 | ||
| 65-69 | poznańskie | Poznań | 28.1 | 2339.6 | ||
| 70-74 | stanisławowskie | Stanisławów | 16.9 | 1480.3 | ||
| 75-79 ? | Auton. śląskie | Katowice | 5.1 | 1533.5 | ||
| 80-84 | tarnopolskie | Tarnopol | 16.5 | 1600.4 | ||
| 90-94 | wileńskie | Wilno | 29.0 | 1276.0 | ||
| 95-99 | wołyńskie | Łuck | 35.7 | 2085.6 | ||
Voivodeships in Congress Poland 1816-1837
From 1816 to 1837 there were 8 voivodeships in Congress Poland.
- Augustów Voivodeship
- Kalisz Voivodeship
- Kraków Voivodeship
- Lublin Voivodeship
- Mazowsze Voivodeship
- Płock Voivodeship
- Podlasie Voivodeship
- Sandomierz Voivodeship
Voivodeships in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth 1569-1795
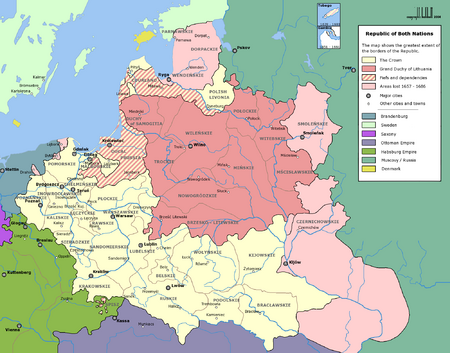
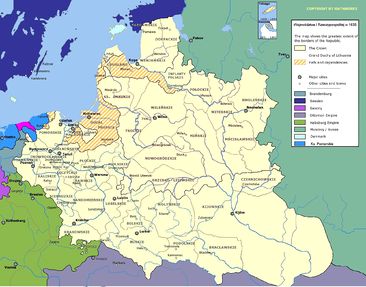
Greater Poland (Wielkopolska)
- Poznań Voivodeship (województwo poznańskie, Poznań)
- Kalisz Voivodeship (województwo kaliskie, Kalisz)
- Gniezno Voivodeship (województwo gnieźnieńskie, Gniezno) from 1768
- Sieradz Voivodeship (województwo sieradzkie, Sieradz)
- Łęczyca Voivodeship (województwo łęczyckie, Łęczyca)
- Brześć Kujawski Voivodeship (województwo brzesko-kujawskie, Brześć Kujawski)
- Inowrocław Voivodeship (województwo inowrocławskie, Inowrocław)
- Chełmno Voivodeship (województwo chełmińskie, Chełmno)
- Malbork Voivodeship (województwo malborskie, Malbork)
- Pomeranian Voivodeship (województwo pomorskie, Gdańsk)
- Duchy of Warmia (Księstwo Warmińskie, Lidzbark Warmiński)
- Duchy of Prussia (Księstwo Pruskie, Lidzbark Warmiński)
- Płock Voivodeship (województwo płockie, Płock)
- Rawa Voivodeship (województwo rawskie, Rawa Mazowiecka)
- Masovian Voivodeship (województwo mazowieckie, Warszawa)
Lesser Poland (Małopolska)
- Kraków Voivodeship (województwo krakowskie, Kraków)
- Sandomierz Voivodeship (województwo sandomierskie, Sandomierz)
- Lublin Voivodeship (województwo lubelskie, Lublin)
- Podlaskie Voivodeship (województwo podlaskie, Drohiczyn)
- Ruthenian Voivodeship (województwo ruskie, Lwów)
- Bełz Voivodeship (województwo belzkie, Bełz)
- Volhynian Voivodeship (województwo wołyńskie, Łuck)
- Podole Voivodeship (województwo podolskie, Kamieniec Podolski)
- Bracław Voivodeship (województwo bracławskie, Bracław)
- Kijów Voivodeship (województwo kijowskie, Kijów)
- Czernihów Voivodeship (województwo czernichowskie, Czernihów)
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Here the first name given is English, then in brackets – Lithuanian, and then Polish.
- Wilno Voivodeship (Vilniaus vaivadija, województwo wileńskie, Vilnius)
- Troki Voivodeship (Trakų vaivadija, województwo trockie, Trakai)
- Nowogródek Voivodeship (Naugarduko vaivadija, województwo nowogrodzkie, Nowogródek)
- Brest-Litovsk Voivodeship (Lietuvos Brastos vaivadija, województwo brzesko-litewskie, Brześć Litewski)
- Minsk Voivodeship (Minsko vaivadija, województwo mińskie, Mińsk)
- Mścisław Voivodeship (Mstslavlio vaivadija, województwo mścisławskie, Mscislaw)
- Smolensk Voivodeship (Smolensko vaivadija, województwo smoleńskie, Smoleńsk)
- Vitebsk Voivodeship (Vitebsko vaivadija, województwo witebskie, Witebsk)
- Połock Voivodeship (Polocko vaivadija, województwo połockie, Połock)
- Duchy of Samogita (Žemaičių seniūnija, księstwo żmudzkie, Medininkai-Varniai)
Duchy of Livonia
- Wenden Voivodeship (województwo wendeńskie, Wenden) since 1598 till the 1620s
- Dorpat Voivodeship (województwo dorpackie, Dorpat) since 1598 till the 1620s
- Parnawa Voivodeship (województwo parnawskie, Parnawa) since 1598 till the 1620s
- Inflanty Voivodeship (województwo inflanckie, Dyneburg) since the 1620s
- Duchy of Courland and Semigalia (księstwo Kurlandii i Semigalii, Mitawa)
Etymology and use of "voivodeship"
Some English-language sources, especially in historic contexts, speak of "palatinates" rather than "voivodeships"; the former term traces back to the Latin palatinus. More commonly used now is the term "voivodeship", a calque of the original Polish term województwo. Other sources refer instead to "provinces", though in pre-1795 contexts this may be misleading since the word "province" (in Polish, prowincja) was applied, until the third and last of the Partitions of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795, to the three main Regions (Greater Poland, Lesser Poland and Lithuania) of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, each of which comprised a number of voivodeships.
The Polish term województwo, designating a second-tier Polish or Polish–Lithuanian administrative unit, derives from wojewoda (etymologically, a "war leader", but now merely the governor of a województwo) and the suffix -stwo (a "state or condition").
The English word "voivodeship", which is a hybrid of voivode and -ship (a suffix likewise meaning a "state or condition") that calques (replicates) those two elements found in the Polish original, has never been much used and is absent from many dictionaries. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, its first use dates from 1792, spelled woiwodship, in the sense of "the district or province governed by a voivode." The word subsequently also appeared, for the first time in 1886, in the sense of "the office or dignity of a voivode."
An official Polish body, the Commission on Standardization of Geographic Names outside the Republic of Poland, recommends use of the spelling "voivodship", without the e. This is consistently reflected in publications[1][2][3] and in the international arena, e.g., at the United Nations.[4]
See also
- Coats of arms of Polish voivodeships
- Flags of Polish voivodeships
- ISO 3166-2:PL
- Voivodeship
References
External links
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
|
|||||||